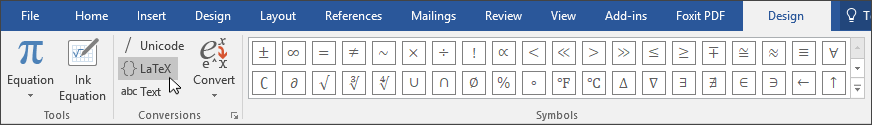
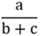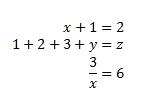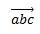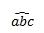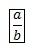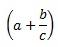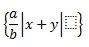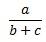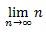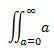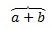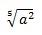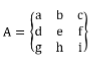To insert an equation using the keyboard, press ALT+ =, and then type the equation.
You can insert equation symbols outside a math region by using Math AutoCorrect. For more information, see Use Math AutoCorrect rules outside of math regions check box.
You can also create math equations using on the keyboard using a combination of keywords and math autocorrect codes. New to Word for Microsoft 365 subscribers is the ability to type math using the LaTeX syntax; details described below.
Linear format is a representation of math on one line in documents. There are two linear formats for math that Word supports:.
-
Unicode math
-
LaTeX math
Depending on your preferred input format, you can create equations in Word in either one of UnicodeMath or LaTeX formats by selecting the format from the Equations tab.
Note: All the other Office applications support only UnicodeMath linear format.
To create a fraction using these different formats with subscript,
-
Enter your equation using Alt + = on the keyboard.
-
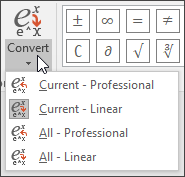
Choose Convert and select professional to build your typed fractions to their Professional form into subscripts, or use Ctrl + =. You can similarly convert an equation back down to a linear format with Ctrl + Shift + =.
Examples
|
Format |
Input |
Output |
|---|---|---|
|
Unicode Math |
a/(b+c) |
|
|
LateX |
\frac{a}{b+c} |
|
Note: Convert a professional format equation format to it's source format, change the convert tool to build a linear format by selecting the desired option from the Convert menu.
UnicodeMath resembles real mathematical notation the most in comparison to all of the math linear formats, and it is the most concise linear format, though some may prefer editing in the LaTeX input over UnicodeMath since that is widely used in academia.
You can type most equations in UnicodeMath quickly by using Math AutoCorrect codes. For example, to align an equation array, you can use @ and &, as in the following:
\eqarray(x+1&=2@1+2+3+y&=z@3/x&=6)<space>
which resolves to:
Here are some other examples:
|
Example |
UnicodeMath format |
Built-up format |
|---|---|---|
|
Vectors |
(abc)\vec<space><space> |
|
|
(abc)\hat<space><space> |
|
|
|
Boxed formula |
\rect(a/b)<space> |
|
|
Brackets |
(a+b/c)<space> |
|
|
{a+b/c}<space> |
|
|
|
Brackets with separators |
{a/b\vbar<space>x+y\vbar<space>}<space> |
|
|
Fractions |
a/(b+c)<space> |
|
|
LeftSubSup |
_a^b<space>x<space> |
|
|
Limit |
lim_(n->\infty)<space>n |
|
|
Matrix |
(\matrix(a&b@c&d))<space> |
|
|
Nary |
\iint_(a=0)^\infty<space><space>a |
|
|
Over/Underbar |
\overbar(abc)<space> |
|
|
\overbrace(a+b)<space> |
|
|
|
Radicals |
\sqrt(5&a^2)<space> |
|
Note: When an example is followed by two consecutive spaces, the first space resolves the typed text into the equation, and the second space builds it up.
Microsoft Office uses the linear format described in Unicode Technical Note 28 to build up and display mathematical expressions. For more information, including how to quickly type up and build equations, see Unicode Nearly Plain-Text Encoding of Mathematics.
LaTeX equation editing supports most of the common LaTeX mathematical keywords. To create a 3x3 matrix equation in the LaTeX format, type the following into a math zone:
A=\{\matrix{a&b&c\\d&e&f\\g&h&j}\}
This will build into the following professional equation:
Here are some other examples of LaTeX expressions that can be built-up into a professional format.
|
Example |
LaTeX Examples |
Built-up format |
|---|---|---|
|
Vectors |
\vec{abc} |
|
|
\hat{abc} |
|
|
|
Boxed formula |
\rect{\frac{a}{b}} |
|
|
Brackets |
\left( a + \frac{b}{c} \right) |
|
|
\left{ a + \frac{b}{c} \right} |
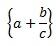 |
|
|
Brackets with separators |
\left{\frac{a}{b}\left|x+y\right|\right} |
|
|
Fractions |
\frac{a}{b+c} |
|
|
LeftSubSup |
{_a^b}x |
|
|
Limit |
\lim\below{n \rightarrow \infty} n |
|
|
Matrix |
\matrix{a & b \\ c & d} |
|
|
Nary |
\iint_{a=0}^{\infty} a |
|
|
Over/Underbar |
\overbar{abc} |
|
|
\overbrace{a+b} |
|
|
|
Radicals |
\sqrt[5]{a^2} |
|
Most LaTeX expressions are supported in this new feature to Word; a list of exceptions is provided below for LaTeX keywords that are not currently supported.
|
Unsupported LaTeX Keywords |
Symbol |
|---|---|
|
\eqarray |
█ |
|
\Middle |
ⓜ |
|
\ldiv |
∕ |
|
\dsmash |
↓ |
Some LaTeX expressions take a slightly different syntax than might be expected.
For example, LaTeX matrices are often created using the following syntax:
\begin{matrix} a & b \\ c & d \end{matrix}
However \begin{} and \end{} keywords are not supported in Word, so instead, a LaTeX matrix input takes simply \matrix{} and would look like:
\matrix{a & b \\ c & d}
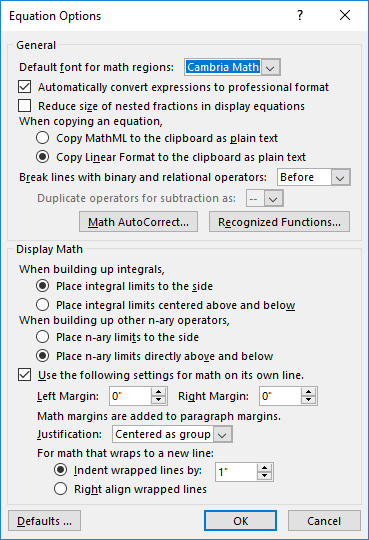
Microsoft Word’s Autocorrect feature simplifies the process of typing mathematical expressions by automatically converting them into a professional format. This functionality is useful when you work in a UnicodeMath mode. You can turn on or turn off this setting by selecting the appropriate box in the Equation Options dialog box.
Type one of the following codes followed by a delimiting term. When entering a code, use a punctuation mark, or press the SPACEBAR or ENTER key. For instance, typing \circ followed by a space will convert to the degree symbol (∘).
Cambria Math is the default font available in the Equations Options dialog box. To ensure consistency, go to the Home tab, and within the Font group, select Cambria Math. This will align the symbols displayed in the document with those in the AutoCorrect box.
Important: The codes are case-sensitive.
Note: For a complete list of symbols supported by Maths AutoCorrect, including their descriptions, Unicode values, and commands, go to Quick start guide to Maths AutoCorrect commands and symbols.
Basic Math
This table includes symbols pertaining to basic mathematics, along with their descriptions and corresponding commands in Word.
|
Symbol |
Symbol Name |
AutoCorrect Command |
|---|---|---|
|
± |
Plus minus |
\pm |
|
∞ |
Infinity |
\infty |
|
= |
Equals |
= |
|
≠ |
Not equal to |
\neq or \ne |
|
~ |
Approximately |
\sim |
|
× |
Multiplication sign |
\times |
|
÷ |
Division sign |
\div |
|
! |
Factorial |
! |
|
∝ |
Proportional to |
\propto |
|
< |
Less Than |
< |
|
≪ |
Much less than |
\ll |
|
> |
Greater than |
> |
|
≫ |
Much greater than |
\gg |
|
≤ |
Less than or equal to |
\leq |
|
≥ |
Greater than or equal to |
\geq or \ge |
|
∓ |
Minus plus |
\mp |
|
≅ |
Approximately equal to |
\cong |
|
≈ |
Almost equal to |
\approx |
|
≡ |
Identical to |
\equiv |
|
∀ |
For all |
\forall |
|
∁ |
Complement |
\complement |
|
∂ |
Partial Differential |
\partial |
|
√ |
Radical Sign |
\sqrt |
|
∛ |
Cube root |
\cbrt |
|
∜ |
Fourth root |
\qdrt |
|
∪ |
Union |
\cup |
|
∩ |
Intersection |
\cap |
|
∅ |
Empty set |
\emptyset |
|
% |
Percentage |
% |
|
° |
Degrees |
\degree |
|
℉ |
Degrees Fahrenheit |
\degf |
|
℃ |
Degrees Celsius |
\degC |
|
∆ |
Increment |
\inc |
|
∇ |
Nabla (Gradient) |
\nabla |
|
∃ |
There exists |
\exists |
|
∄ |
There does not exist |
\nexists |
|
∈ |
Element of |
\in |
|
∋ |
Contains as member |
\ni |
|
← |
Left arrow |
\leftarrow or \gets |
|
↑ |
Upward Arrow |
\uparrow |
|
→ |
Right arrow |
\rightarrow |
|
↓ |
Downward arrow |
\downarrow |
|
↔ |
Left-right arrow |
\leftrightarrow |
|
∴ |
Therefore |
\therefore |
|
+ |
Plus |
+ |
|
− |
Minus |
\- |
|
¬ |
Not sign |
\neg |
|
α |
Alpha |
\alpha |
|
β |
Beta |
\beta |
|
γ |
Gamma |
\gamma |
|
δ |
Delta |
\delta |
|
ε |
Epsilon |
\epsilon |
|
ϵ |
Variant Epsilon |
\varepsilon |
|
θ |
Theta |
\theta |
|
ϑ |
Variant Theta |
\vartheta |
|
μ |
Mu |
\mu |
|
π |
Pi |
\pi |
|
ρ |
Rho |
\rho |
|
σ |
Sigma |
\sigma |
|
τ |
Tau |
\tau |
|
φ |
Phi |
\phi |
|
ω |
Omega |
\omega |
|
∗ |
Asterisk Operator |
\ast |
|
∙ |
Bullet operator |
\bullet |
|
⋮ |
Vertical ellipsis |
\vdots |
|
⋯ |
Midline Horizontal Ellipsis |
\cdots |
|
⋰ |
Upward Right Diagonal Ellipsis |
\rddots |
|
⋱ |
Downward Right Diagonal Ellipsis |
\ddots |
|
ℵ |
Aleph |
\aleph |
|
ℶ |
Beth (Second infinite cardinal) |
\beth |
|
∎ |
End of proof (Q.E.D.) |
\qed |
Greek Letters
This table includes symbols pertaining to Greek Letters, along with their descriptions and corresponding commands in Word.
|
Symbol |
Symbol Name |
AutoCorrect Command |
|---|---|---|
|
α |
Alpha (lowercase) |
\alpha |
|
β |
Beta (lowercase) |
\beta |
|
γ |
Gamma (lowercase) |
\gamma |
|
δ |
Delta (lowercase) |
\delta |
|
ε |
Epsilon (lowercase) |
\epsilon |
|
ϵ |
Variant Epsilon (lowercase) |
\varepsilon |
|
ζ |
Zeta (lowercase) |
\zeta |
|
η |
Eta (lowercase) |
\eta |
|
θ |
Theta (lowercase) |
\theta |
|
ϑ |
Variant Theta (lowercase) |
\vartheta |
|
ι |
Iota (lowercase) |
\iota |
|
κ |
Kappa (lowercase) |
\kappa |
|
λ |
Lambda (lowercase) |
\lambda |
|
μ |
Mu (lowercase) |
\mu |
|
ν |
Nu (lowercase) |
\nu |
|
ξ |
Xi (lowercase) |
\xi |
|
ο |
Omicron (lowercase) |
\omicron |
|
π |
Pi (lowercase) |
\pi |
|
ϖ |
Variant Pi (lowercase) |
\varpi |
|
ρ |
Rho (lowercase) |
\rho |
|
ϱ |
Variant Rho (lowercase) |
\varrho |
|
σ |
Sigma (lowercase) |
\sigma |
|
ς |
Variant Sigma (lowercase) |
\varsigma |
|
τ |
Tau (lowercase) |
\tau |
|
υ |
Upsilon (lowercase) |
\upsilon |
|
φ |
Phi (lowercase) |
\phi |
|
ϕ |
Variant Phi (lowercase) |
\varphi |
|
χ |
Chi (lowercase) |
\chi |
|
ψ |
Psi (lowercase) |
\psi |
|
ω |
Omega (lowercase) |
\omega |
|
Α |
Alpha (uppercase) |
\Alpha |
|
Β |
Beta (uppercase) |
\Beta |
|
Γ |
Gamma (uppercase) |
\Gamma |
|
Δ |
Delta (uppercase) |
\Delta |
|
Ε |
Epsilon (uppercase) |
\Epsilon |
|
Ζ |
Zeta (uppercase) |
\Zeta |
|
Η |
Eta (uppercase) |
\Eta |
|
Θ |
Theta (uppercase) |
\Theta |
|
Ι |
Iota (uppercase) |
\Iota |
|
Κ |
Kappa (uppercase) |
\Kappa |
|
Λ |
Lambda (uppercase) |
\Lambda |
|
Μ |
Mu (uppercase) |
\Mu |
|
Ν |
Nu (uppercase) |
\Nu |
|
Ξ |
Xi (uppercase) |
\Xi |
|
Ο |
Omicron (uppercase) |
\Omicron |
|
Π |
Pi (uppercase) |
\Pi |
|
Ρ |
Rho (uppercase) |
\Rho |
|
Σ |
Sigma (uppercase) |
\Sigma |
|
Τ |
Tau (uppercase) |
\Tau |
|
Υ |
Upsilon (uppercase) |
\Upsilon |
|
Φ |
Phi (uppercase) |
\Phi |
|
Χ |
Chi (uppercase) |
\Chi |
|
Ψ |
Psi (uppercase) |
\Psi |
|
Ω |
Omega (uppercase) |
\Omega |
Letter-Like Symbols
This table includes symbols pertaining to Letter-Like Symbols, along with their descriptions and corresponding commands in Word.
|
Symbol |
Symbol Name |
AutoCorrect Command |
|---|---|---|
|
∀ |
For all |
\forall |
|
∁ |
Complement |
\complement |
|
ℂ |
Double-struck C |
\doubleC |
|
∂ |
Partial differential |
\partial |
|
ð |
Latin small letter Eth |
n/a |
|
ℇ |
Euler Constant |
n/a |
|
Ϝ |
Greek Capital Digamma |
n/a |
|
Ⅎ |
Turned Capital F |
n/a |
|
ℊ |
Script small G |
\scriptg |
|
ℋ |
Script Capital H |
\scriptH |
|
ℌ |
Hilbert Space |
\frakturH |
|
ℎ |
Planck Constant |
n/a |
|
ℏ |
Planck Constant over Two Pi |
\hbar |
|
℩ |
Turned Greek Letter Small Iota |
n/a |
|
ı |
Latin small letter dotless I |
n/a |
|
ℑ |
Imaginary Part |
\frakturI or \lm |
|
j |
Latin Small Letter J |
n/a |
|
ϰ |
Greek Kappa Symbol |
n/a |
|
ℒ |
Laplace Transform |
\scriptL |
|
ℓ |
Script Small L |
\scriptl |
|
ℕ |
Natural numbers |
\mathbb{N} |
|
℘ |
Weierstrass p |
\wp |
|
ℚ |
Rational numbers |
\mathbb{Q} |
|
ℛ |
Script R |
\mathscr{R} |
|
ℜ |
Real part |
\frakturR or \Re |
|
ℝ |
Real numbers |
\mathbb{R} |
|
ℤ |
Integers |
\mathbb{Z} |
|
℧ |
Inverted ohm (mho) |
\mho |
|
Å |
Angstrom |
\AA |
|
ℬ |
Script B |
\mathscr{B} |
|
℮ |
Estimated symbol |
\euro (not exact) |
|
ℰ |
Script E |
\mathscr{E} |
|
∃ |
There exists |
\exists |
|
∄ |
There does not exist |
\nexists |
|
ℱ |
For all |
\mathscr{F} |
|
ℳ |
Script M |
\mathscr{M} |
|
ℴ |
Script O (small) |
\mathscr{o} |
|
ℵ |
Aleph |
\aleph |
|
ℶ |
Bet (second transfinite cardinal) |
\beth |
|
ℷ |
Gimel (third transfinite cardinal) |
\gimel |
|
ℸ |
Dalet (fourth transfinite cardinal) |
\daleth |
Common Binary Operators
This table includes symbols pertaining to Common Binary Operators, along with their descriptions and corresponding commands in Word.
|
Symbol |
Symbol Name |
AutoCorrect Command |
|---|---|---|
|
+ |
Plus |
+ |
|
− |
Minus |
\- |
|
÷ |
Division Sign |
\div |
|
× |
Multiplication Sign |
\times |
|
± |
Plus Minus |
\pm |
|
∓ |
Minus Plus |
\mp |
|
∝ |
Proportional To |
\propto |
|
∕ |
Division Slash |
\ldiv |
|
∗ |
Asterisk Operator |
\ast |
|
∘ |
Ring Operator |
\circ |
|
∙ |
Bullet Operator |
\bullet |
|
⋅ |
Dot Operator |
\cdot |
|
∩ |
Intersection |
\cap |
|
∪ |
Union |
\cup |
|
⊎ |
Multiset Union |
\uplus |
|
⊓ |
Square Cap |
\sqcap |
|
⊔ |
Square Cup |
\sqcup |
|
∧ |
Logical AND |
\wedge |
|
∨ |
Logical OR |
\vee |
Basic N-ary Operators
This table includes symbols pertaining to Basic N-ary Operators, along with their descriptions and corresponding commands in Word.
|
Symbol |
Symbol Name |
AutoCorrect Command |
|---|---|---|
|
∑ |
Summation |
\sum |
|
∫ |
Integral |
\int |
|
∬ |
Double Integral |
\iint |
|
∭ |
Triple Integral |
\iiint |
|
∮ |
Contour Integral |
\oint |
|
∯ |
Surface Integral |
\oiint |
|
∰ |
Volume Integral |
\oiiint |
|
∱ |
Clockwise Integral |
\cwint |
|
∲ |
Clockwise Contour Integral |
\coint |
|
∳ |
Anticlockwise Contour Integral |
\aoint |
|
∏ |
Product |
\prod |
|
∐ |
Coproduct |
\amalg |
|
⋂ |
N-ary Intersection |
\bigcap |
|
⋃ |
N-ary Union |
\bigcup |
|
⋀ |
N-ary Logical And |
\bigwedge |
|
⋁ |
N-ary Logical Or |
\bigvee |
|
⨀ |
N-ary Circled Dot Operator |
\bigodot |
|
⨂ |
N-ary Circled Times Operator |
\bigotimes |
|
⨄ |
N-ary Union Operator with Plus |
\biguplus |
|
⨃ |
N-ary Intersection Operator with Dot |
\bigcapdot |
Advanced Binary Operators
This table includes symbols pertaining to Advanced Binary Operators, along with their descriptions and corresponding commands in Word.
|
Symbol |
Symbol Name |
AutoCorrect Command |
|---|---|---|
|
∔ |
Dot Plus |
\dotplus |
|
∸ |
Dot Minus |
\dotminus |
|
∖ |
Set Minus (Backslash) |
\setminus |
|
⋒ |
Double Intersection |
\Cap |
|
⋓ |
Double Union |
\Cup |
|
⊟ |
Squared Minus |
\boxminus |
|
⊠ |
Squared Times |
\boxtimes |
|
⊡ |
Squared Dot Operator |
\boxdot |
|
⊞ |
Squared Plus |
\boxplus |
|
⋇ |
Division Times |
\divideontimes |
|
⋉ |
Left Normal Factor Semidirect Product |
\ltimes |
|
⋊ |
Right Normal Factor Semidirect Product |
\rtimes |
|
⋋ |
Left Semidirect Product |
\leftthreetimes |
|
⋌ |
Right Semidirect Product |
\rightthreetimes |
|
⋏ |
Curly Logical And |
\curlywedge |
|
⋎ |
Curly Logical OR |
\curlyvee |
|
⊝ |
Circled Dash |
\ominus |
|
⊺ |
Intercalate |
\intercal |
|
⊕ |
Circled Plus |
\oplus |
|
⊖ |
Circled Minus |
\ominus |
|
⊗ |
Circled Times |
\otimes |
|
⊘ |
Circled Division Slash |
\oslash |
|
⊙ |
Circled Dot Operator |
\odot |
|
⊛ |
Circled Asterisk Operator |
\oast |
|
⊚ |
Circled Ring Operator |
\ocirc |
|
† |
Dagger |
\dagger |
|
‡ |
Double Dagger |
\ddag |
|
⋆ |
Star Operator |
\star |
|
⋄ |
Diamond Operator |
\diamond |
|
≀ |
Wreath Product |
\wr |
|
△ |
White up-pointing triangle |
\triangle |
|
⋀ |
N-ary Logical AND |
\bigwedge |
|
⋁ |
N-ary Logical OR |
\bigvee |
|
⨀ |
N-ary Circled Dot Operator |
\bigodot |
|
⨂ |
N-ary Circled Times Operator |
\bigotimes |
|
⨁ |
N-ary Circled Plus Operator |
\bigoplus |
|
⨅ |
N-Ary Square Intersection Operator |
\bigsqcap |
|
⨆ |
N-Ary Square Union Operator |
\bigsqcup |
|
⨄ |
N-ary Union operator with plus |
\biguplus |
|
⨃ |
N-ary Union operator with dot |
n/a |
Common Relational Operators
This table includes symbols pertaining to Common Relational Operators, along with their descriptions and corresponding commands in Word.
|
Symbol |
Symbol Name |
AutoCorrect Command |
|---|---|---|
|
= |
Equals |
= |
|
≠ |
Not equal |
\neq or \ne |
|
< |
Less than |
< |
|
> |
Greater than |
> |
|
≤ |
Less than or equal |
\leq |
|
≥ |
Greater than or equal |
\geq or \ge |
|
≮ |
Not less than |
\nless |
|
≰ |
Not less than or equal |
\nleq |
|
≯ |
Not greater than |
\ngt |
|
≱ |
Not greater than or equal |
\ngeq |
|
≡ |
Identical to |
\equiv |
|
∼ |
Tilde (similar to) |
\sim |
|
≃ |
Asymptotically equal to |
\simeq |
|
≈ |
Almost equal to |
\approx |
|
≅ |
Congruent to |
\cong |
|
≢ |
Not identical to |
\nequiv |
|
≄ |
Not asymptotically equal |
\nsimeq |
|
≉ |
Not almost equal to |
\napprox |
|
≇ |
Neither Approximately Nor Actually Equal To |
\ncong |
|
∝ |
Proportional to |
\propto |
|
≪ |
Much less than |
\ll |
|
≫ |
Much greater than |
\gg |
|
∈ |
Element of |
\in |
|
∋ |
Contains as member |
\ni |
|
∉ |
Not an element of |
\notin |
|
⊂ |
Subset of |
\subset |
|
⊃ |
Superset of |
\supset |
|
⊆ |
Subset of or equal to |
\subseteq |
|
⊇ |
Superset of or equal to |
\supseteq |
|
≺ |
Precedes |
\prec |
|
≻ |
Succeeds |
\succ |
|
≼ |
Precedes or equal to |
\preceq |
|
≽ |
Succeeds or equal to |
\succeq |
|
⊏ |
Square subset |
\sqsubset |
|
⊐ |
Square superset |
\sqsupset |
|
⊑ |
Square subset or equal |
\sqsubseteq |
|
⊒ |
Square superset or equal |
\sqsupseteq |
|
∥ |
Parallel to |
\parallel |
|
⊥ |
Perpendicular to |
\perp or \bot |
|
⊢ |
Proves |
\vdash |
|
⊣ |
Does Not Yield |
\dashv |
|
⋈ |
Natural join |
\bowtie |
|
≍ |
Approximately equal or image of |
\asymp |
Advanced Relational Operators
This table includes symbols pertaining to Advanced Relational Operators, along with their descriptions and corresponding commands in Word.
|
Symbol |
Symbol Name |
AutoCorrect Command |
|---|---|---|
|
∴ |
Therefore |
\therefore |
|
∵ |
Because |
\because |
|
⋘ |
Very much less than |
\lll |
|
⋙ |
Very much greater than |
\ggg |
|
≦ |
Less than over equal to |
\leqq |
|
≧ |
Greater than over equal to |
\geqq |
|
≲ |
Less than and similar to |
\lesssim |
|
≳ |
Greater than and similar to |
\gtrsim |
|
⋖ |
Less than with dot |
\lessdot |
|
⋗ |
Greater than with dot |
\gtrdot |
|
≶ |
Less than or greater than |
\lessgtr |
|
⋚ |
Less than but not equivalent to |
\lesseqgtr |
|
≷ |
Greater than or less than |
\gtrless |
|
⋛ |
Greater than but not equivalent to |
\gtreqless |
|
≑ |
Geometrically equal to |
\Doteq |
|
≒ |
Approximately equal to or image of |
\fallingdotseq |
|
≓ |
Image of or approximately equal to |
\risingdotseq |
|
∽ |
Reversed tilde |
\backsim |
|
≊ |
Almost equal or equivalent |
\approxeq |
|
⋍ |
Reversed tilde equals |
\backsimeq |
|
≼ |
Precedes or equal to |
\preceq |
|
≽ |
Succeeds or equal to |
\succeq |
|
⋞ |
Equal To or Precedes |
\eqless |
|
⋟ |
Equal To or Succeeds |
\eqgtr |
|
≾ |
Precedes but not equivalent |
\precsim |
|
≿ |
Succeeds or equivalent to |
\succsim |
|
⋜ |
Equal to or less than |
\eqless |
|
⋝ |
Equal to or greater than |
\eqgtr |
|
⊆ |
Subset of or equal to |
\subseteq |
|
⊇ |
Superset of or equal to |
\supseteq |
|
⊲ |
Normal subgroup of |
\vartriangleleft |
|
⊳ |
Contains as Normal Subgroup |
\vartriangleright |
|
⊴ |
Normal subgroup or equal to |
\trianglelefteq |
|
⊵ |
Contains as Normal Subgroup or equal to |
\trianglerighteq |
|
⊨ |
True, models |
\models |
|
⋐ |
Nested subset |
\Subset |
|
⋑ |
Nested superset |
\Supset |
|
⊏ |
Square subset |
\sqsubset |
|
⊐ |
Square superset |
\sqsupset |
|
⊩ |
Double vertical bar with turnstile |
\vDash |
|
⊪ |
Triple vertical bar with turnstile |
\Vvdash |
|
≖ |
Circle with equals sign |
\eqcirc |
|
≗ |
Ring Equal To |
\circeq |
|
≜ |
Delta Equal To |
\Deltaeq |
|
≏ |
Difference between |
\bumpe |
|
≎ |
Geometrically equivalent to |
\bumpeq |
|
∝ |
Proportional to |
\propto |
|
≬ |
Between |
\between |
|
⋔ |
Pitchfork |
\pitchfork |
|
≐ |
Approaches the limit |
\doteq |
|
⋈ |
Bowtie |
\bowtie |
Arrows
This table includes symbols pertaining to Arrows, along with their descriptions and corresponding commands in Word.
|
Symbol |
Symbol Name |
AutoCorrect Command |
|---|---|---|
|
← |
Left Arrow |
\leftarrow or \gets |
|
→ |
Right Arrow |
\rightarrow |
|
↑ |
Upward Arrow |
\uparrow |
|
↓ |
Downward Arrow |
\downarrow |
|
↔ |
Left-Right Arrow |
\leftrightarrow |
|
↕ |
Up-Down Arrow |
\updownarrow |
|
⇐ |
Left Double Arrow |
\Leftarrow |
|
⇒ |
Right Double Arrow |
\Rightarrow |
|
⇑ |
Upward Double Arrow |
\Uparrow |
|
⇓ |
Downward Double Arrow |
\Downarrow |
|
⇔ |
Left-Right Double Arrow |
\Leftrightarrow |
|
⇕ |
Up-Down Double Arrow |
\Updownarrow |
|
⟵ |
Long Left Arrow |
\longleftarrow |
|
⟶ |
Long Right Arrow |
\longrightarrow |
|
⟷ |
Long Left-Right Arrow |
\longleftrightarrow |
|
⟸ |
Long Left Double Arrow |
\Longleftarrow |
|
⟹ |
Long Right Double Arrow |
\Longrightarrow |
|
⟺ |
Long Left-Right Double Arrow |
\Longleftrightarrow |
|
↗ |
Diagonal Upward Right Arrow |
\nearrow |
|
↖ |
Diagonal Upward Left Arrow |
\nwarrow |
|
↘ |
Diagonal Downward Right Arrow |
\searrow |
|
↙ |
Diagonal Downward Left Arrow |
\swarrow |
|
↚ |
Left Arrow with Stroke |
\nleftarrow |
|
↛ |
Right Arrow with Stroke |
\nrightarrow |
|
↮ |
Left-Right Arrow with Stroke |
\nleftrightarrow |
|
⇍ |
Left Double Arrow with Stroke |
\nLeftarrow |
|
⇏ |
Right Double Arrow with Stroke |
\nRightarrow |
|
⇎ |
Left Right Double Arrow with Stroke |
\nLeftrightarrow |
|
⇠ |
Left Dashed Arrow |
\dasharrowleft |
|
⇢ |
Right Dashed Arrow |
\dasharrowright |
|
↤ |
Left Arrow from Bar |
\mapstoleft |
|
↦ |
Right Arrow from Bar |
\mapsto |
|
⟻ |
Long Left Arrow from Bar |
\longmapstoleft |
|
⟼ |
Long Right Arrow from Bar |
\longmapsto |
|
↩ |
Left Arrow with Hook |
\hookleftarrow |
|
↪ |
Right Arrow with Hook |
\hookrightarrow |
|
↼ |
Left Harpoon with Barb Facing Upwards |
\leftharpoonup |
|
↽ |
Left Harpoon with Barb Facing Downwards |
\leftharpoondown |
|
⇀ |
Right Harpoon with Barb Facing Upwards |
\rightharpoonup |
|
⇁ |
Right Harpoon with Barb Facing Downwards |
\rightharpoondown |
|
↿ |
Upward Harpoon with Barb on Left |
\upharpoonleft |
|
↾ |
Upward Harpoon with Barb on Right |
\upharpoonright |
|
⇃ |
Downward Harpoon with Barb on Left |
\downharpoonleft |
|
⇂ |
Downward Harpoon with Barb on Right |
\downharpoonright |
|
⇋ |
Left Harpoon Over Right Harpoon |
\leftrightharpoons |
|
⇌ |
Right Harpoon Over Left Harpoon |
\rightleftharpoons |
|
⇇ |
Left paired arrows |
\leftleftarrows |
|
⇉ |
Right paired arrows |
\rightrightarrows |
|
⇈ |
Upwards paired arrows |
\upuparrows |
|
⇊ |
Downwards paired arrows |
\downarrows |
|
⇆ |
Left Arrow Over Right Arrow |
\leftrightarrows |
|
⇄ |
Right Arrow Over Left Arrow |
\rightleftarrows |
|
↫ |
Left Arrow with Loop |
\looparrowleft |
|
↬ |
Right Arrow with Loop |
\looparrowright |
|
↢ |
Left Arrow with Tail |
\leftarrowtail |
|
↣ |
Right Arrow with Tail |
\rightarrowtail |
|
↰ |
Upward Arrow with Tip on Left |
\Lsh |
|
↱ |
Upward Arrow with Tip on Right |
\Rsh |
|
↲ |
Downward Arrow with Tip on Left |
\ldsh |
|
↳ |
Downward Arrow with Tip on Right |
\rdsh |
|
⇚ |
Left Triple Arrow |
\Lleftarrow |
|
⇛ |
Right Triple Arrow |
\Rrightarrow |
|
↞ |
Left Two-Headed Arrow |
\twoheadleftarrow |
|
↠ |
Right Two-Headed Arrow |
\twoheadrightarrow |
|
↶ |
Anticlockwise Top Semicircle Arrow |
\curvearrowleft |
|
↷ |
Clockwise Top Semicircle Arrow |
\curvearrowright |
|
↺ |
Counterclockwise Open Semicircle Arrow |
\circlearrowleft |
|
↻ |
Clockwise Open Semicircle Arrow |
\circlearrowright |
|
⊸ |
Multimap |
\multimap |
|
↭ |
Left-Right Wave Arrow |
\leftrightwavearrow |
|
↜ |
Left Wave Arrow |
\leftwavearrow |
|
↝ |
Right Wave Arrow |
\rightwavearrow |
|
⇜ |
Left Squiggle Arrow |
\leftsquigarrow |
|
⇝ |
Right Squiggle Arrow |
\rightsquigarrow |
Negated Relations
This table includes symbols pertaining to Negated Relations, along with their descriptions and corresponding commands in Word.
|
Symbol |
Symbol Name |
AutoCorrect Command |
|---|---|---|
|
≠ |
Not Equal To |
\neq or \ne |
|
≮ |
Not Less Than |
\nless |
|
≯ |
Not Greater Than |
\ngt |
|
≰ |
Not Less Than or Equal To |
\nleq |
|
≱ |
Not Greater Than or Equal To |
\ngeq |
|
≢ |
Not Identical To |
\nequiv |
|
≁ |
Not Tilde |
\nsim |
|
≄ |
Not Asymptotically Equal To |
\nsimeq |
|
≉ |
Not Almost Equal To |
\napprox |
|
≇ |
Neither Approximately Nor Actually Equal To |
\ncong |
|
≭ |
Not Equivalent To |
\nasymp |
|
≨ |
Less-Than But Not Equal To |
\lneqq |
|
≩ |
Greater-Than But Not Equal To |
\gneqq |
|
⊀ |
Does Not Precede |
\nprec |
|
⊁ |
Does Not Succeed |
\nsucc |
|
⋠ |
Does Not Precede or Equal |
\npreceq |
|
⋡ |
Does Not Succeed or Equal |
\nsucceq |
|
∉ |
Not an Element Of |
\notin |
|
∌ |
Not Contains As Member |
\notni |
|
⊄ |
Not a Subset Of |
\nsub |
|
⊅ |
Not a Superset Of |
\nsup |
|
⊈ |
Not a Subset Of or Equal To |
\nsubseteq |
|
⊉ |
Not a Superset Of or Equal To |
\nsupseteq |
|
⊊ |
Subset Of with Not Equal To |
\succnsim |
|
⊋ |
Superset Of with Not Equal To |
\supsetneq |
|
⋢ |
Not Square Subset or Equal To |
\nsqsubseteq |
|
⋣ |
Not Square Superset |
\nsqsupseteq |
|
⋦ |
Less-Than But Not Equivalent To |
\lnsim |
|
⋧ |
Greater-Than But Not Equivalent To |
\gnsim |
|
⋨ |
Precedes But Not Equivalent To |
\precnsim |
|
⋩ |
Succeeds But Not Equivalent To |
\succnsim |
|
⋪ |
Not Normal Subgroup Of |
\ntriangleleft |
|
⋫ |
Does Not Contain as Normal Subgroup Of |
\ntrianglerighteq |
|
⋬ |
Not Normal Subgroup Of or Equal To |
\ntrianglelefteq |
|
⋭ |
Does Not Contain As Normal Subgroup or Equal To |
\ntrianglerighteq |
|
∤ |
Does Not Divide |
\nmid |
|
∦ |
Not Parallel |
\nparallel |
|
⊬ |
Does Not Prove |
\nvdash |
|
⊭ |
Not True |
\nvDash |
|
⊮ |
Does Not Force |
\nVdash |
|
⊯ |
Negated Double Vertical Bar Double Right Turnstile |
\nVDash |
|
∄ |
There Does Not Exist |
\nexists |
Geometry
This table includes symbols pertaining to Geometry, along with their descriptions and corresponding commands in Word.
|
Symbol |
Symbol Name |
AutoCorrect Command |
|---|---|---|
|
∟ |
Right Angle |
\rightangle |
|
∠ |
Angle |
\angle |
|
∡ |
Measured Angle |
\angmsd |
|
∢ |
Spherical Angle |
\angsph |
|
⊾ |
Right Angle with Arc |
\angrtvb |
|
⊿ |
Right Triangle |
n/a |
|
⋕ |
Equal and Parallel To |
n/a |
|
⊥ |
Perpendicular to |
\perp or \bot |
|
∤ |
Does Not Divide |
\nmid |
|
∥ |
Parallel To |
\parallel |
|
∦ |
Not Parallel To |
\nparallel |
|
∶ |
Ratio |
\ratio |
|
∷ |
Proportion |
\Colon |
|
∴ |
Therefore |
\therefore |
|
∵ |
Because |
\because |
|
∎ |
End of Proof (Q.E.D.) |
\qed |
Note: For information on inserting a symbol that is not in the chart above, see Insert a check mark or other symbol.
-
Click File > Options.
-
Click Proofing, and then click AutoCorrect Options.
-
Click the Math AutoCorrect tab.
-
Select the Use Math AutoCorrect rules outside of math regions check box.